Oct 27, 2022
CMU 15-445: 7. Join Algorithms
7. Join Algorithms
- 为什么需要 join
由于为消除 table 中信息的冗余,我们会采取normalize来使得数据库 table 的设计符合一定范式,但是之后需要使用join来重建原来的 tuple
一般使用inner equijoin,inner equijoin连接两张表中 key 相同的 tuple。其他 join 算法可以通过该算法调整得到
7.1. Join operator output
- copy outer 和 inner tuples 的 attributes into a new tuple.
- Subsequent operators in the query plan never need to go back to the base tables to get more data.
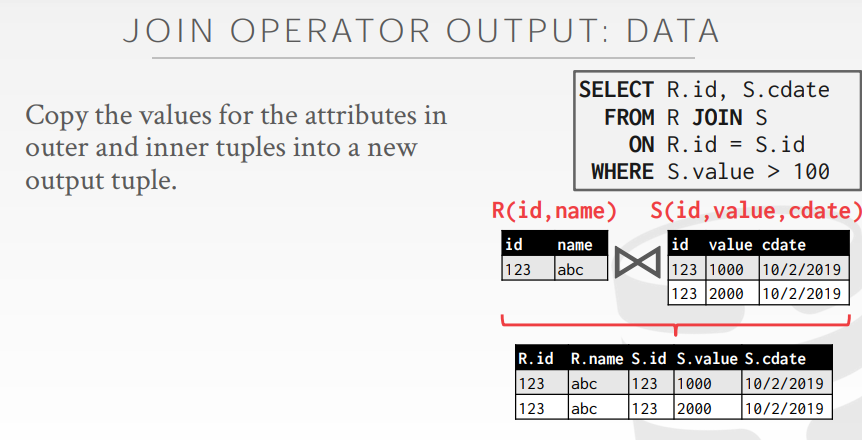
两种处理方式
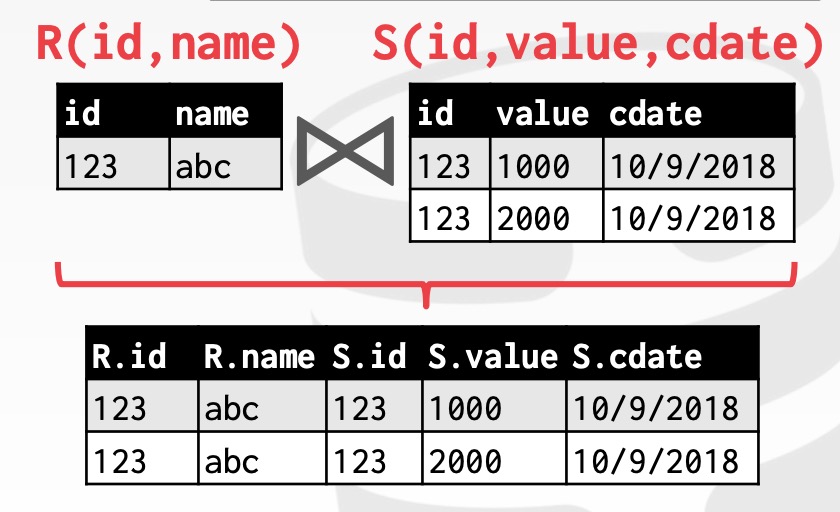
- 可以在 Join 的时候将所有非 Join Attributes 都放入新的 tuple 中,这样 Join 之后的操作都不需要从 tables 中重新获取数据
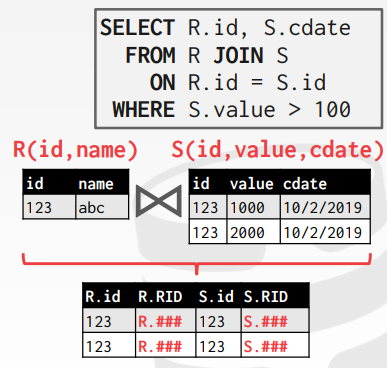
- 也可以在 Join 的时候只复制 Join Attributes 以及 record id,后续操作自行根据 record id 去 tables 中获取相关数据。对于列存储数据库,这是比较理想的处理方式,被称为 Late Materialization。
7.2. Cost analysis
- 由于数据库中的数据量通常较大,无法一次性载入内存,因此 Join Algorithm 的设计目的,在于减少磁盘 I/O,因此我们衡量 Join Algorithm 好坏的标准,就是 I/O 的数量。此外我们不需要考虑 Join 结果的大小,因为不论使用怎样的 Join Algorithm,结果集的大小都一样。
- 用笛卡尔积加谓词筛选实现 join 非常低效

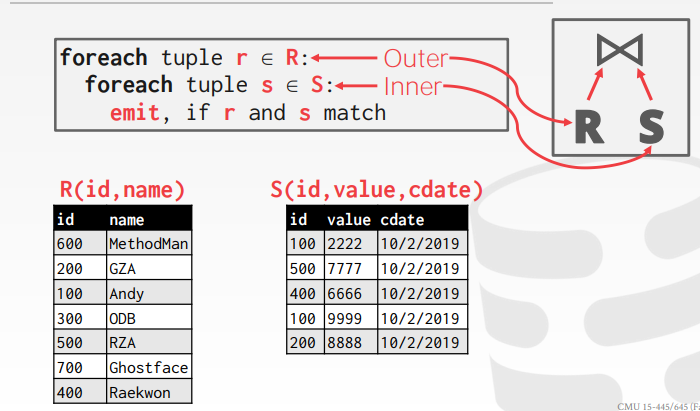
7.3. Nested Loop Join
7.3.1. 分类
- 其实就是嵌套 for 循环
- Stupid nested loop join
- 效率极其低下
- Block nested loop join
- 更少的磁盘 IO
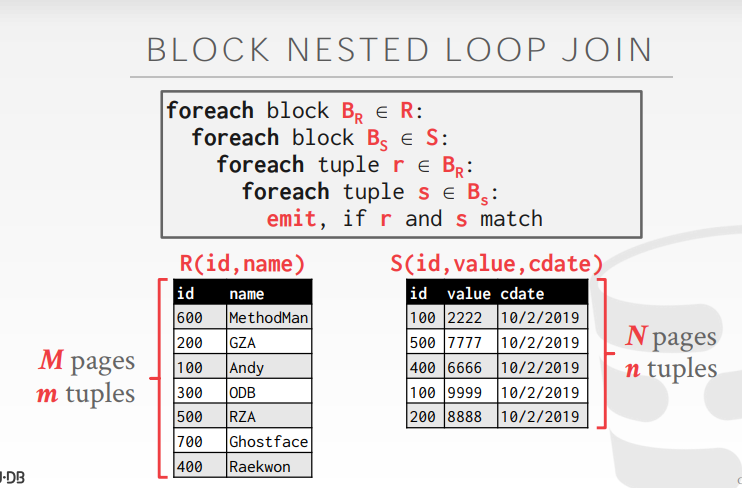
- Index nested loop join
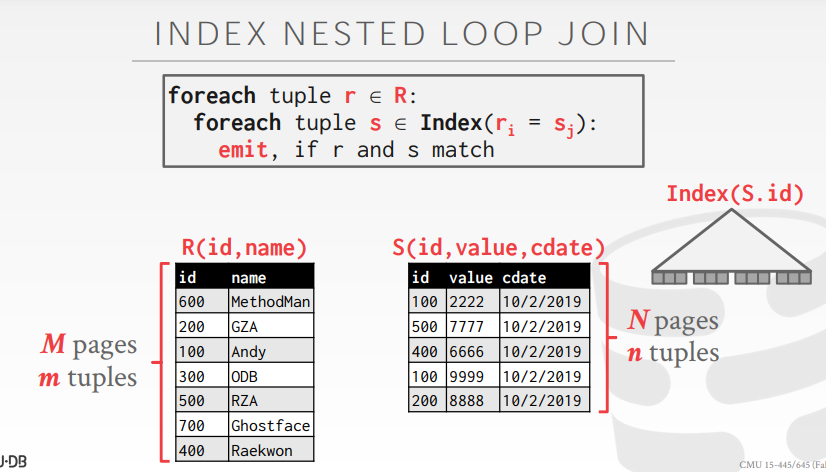
7.3.2. 总结
- 总是选择较小的 table 作为 outer table(因为较小 table 是作为乘数)
- 尽可能多的缓存 outer table 到 buffer 里
- 扫描 Inner Table 时,尽量使用索引
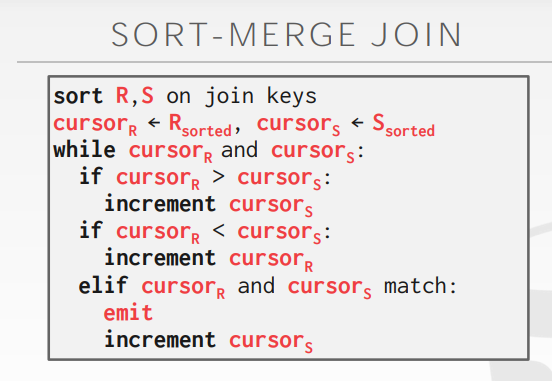
7.4. Sort-Merge Join
7.4.1. Sort
- 对 join key(s)进行排序
7.4.2. Merge
- 用 cursors 扫描两个排好序的表,然后 emit key(s)匹配的 tuples
7.5. Hash Join
7.5.1. Build
- 扫描外表,然后使用哈希函数h1在 join attributes 上生成一个哈希表
7.5.2. Probe
- 扫描内标,然后在每个 tuple 上使用h1,跳转到哈希表上并找到匹配的 tuple
